This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
liyang pushed a commit to branch kylin5
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/kylin.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/kylin5 by this push:
new c7ba38e0b0 update readme for 5.0
c7ba38e0b0 is described below
commit c7ba38e0b0bd0bc1d035eb2920506c07b1b42d6e
Author: lionelcao <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Tue Oct 1 12:57:55 2024 +0800
update readme for 5.0
---
README.md | 152 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++---------
1 file changed, 132 insertions(+), 20 deletions(-)
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index d67208c362..d20edc8712 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,31 +1,143 @@
-## Intro to Kylin 5
+<div align="left">
-### Comparison with Kylin 4.0
+# Apache Kylin
-- New metadata design [New metadata design article (Chinese
ver)](https://kylin.apache.org/5.0/blog/introduction_of_metadata_cn) and [New
metadata
definition](https://github.com/apache/kylin/blob/doc5.0/website/blog/2022-12-18-Introduction_of_Metadata/protocol-buffer/metadata.proto)
-- Support Table Index
-- Support schema change
-- Support computed column
-- New CuboidScheduler
-- New Job engine etc.
+[](https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html)
+[](https://github.com/apache/kylin/releases)
+[](https://github.com/apache/kylin/commits/kylin5/)
+[](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/overview)
-For more detail, please check our
[roadmap](https://kylin.apache.org/5.0/docs/development/roadmap) .
+<div>
-### Quick Start
+[](https://kylin.apache.org/)
+[](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/download)
-1. Build maven artifact with following command:
-```shell
-mvn clean package -DskipTests
-```
+</div>
+</div>
-2. Run unit test with following command:
+---
+Apache Kylin is a leading open source OLAP engine for Big Data capable for
sub-second query latency on trillions of records. Since being created and open
sourced by eBay in 2014, and graduated to Top Level Project of Apache Software
Foundation in 2015.
+Kylin has quickly been adopted by thousands of organizations world widely as
their critical analytics application for Big Data.
-```shell
-sh dev-support/unit_testing.sh
-```
+Kylin has following key strengths:
+
+- High qerformance, high concurrency, sub-second query latency
+- Unified big data warehouse architecture
+- Seamless integration with BI tools
+- Comprehensive and enterprise-ready capabilities
+
+
+
+
+## What's New in Kylin 5.0
+
+---
+
+### 📊 1. Internal Table
+Kylin now support internal table, which is designed for flexible query and
lakehouse scenarios.
+
+### 🦁 2. Model & Index Recommendation
+
+With recommendation engine, you don't have to be an expert of modeling. Kylin
now can auto modeling and optimizing indexes from you query history.
+You can also create model by importing sql text.
+
+### 👾 3. Native Compute Engine
+
+Start from version 5.0, Kylin has integrated Gluten-Clickhosue
Backend(incubating in apache software foundation) as native compute engine. And
use Gluten mergetree as the default storage format of internal table.
+Which can bring 2~4x performance improvement compared with vanilla spark. Both
model and internal table queries can get benefits from the Gluten integration.
-3. Build a Kylin 5 binary
+### 🧜🏻♀️ 4. Streaming Data Source
+
+Kylin now support Apache Kafka as streaming data source of model building.
Users can create a fusion model to implement streaming-batch hybrid analysis.
+
+## Significant Change
+
+---
+
+### 🤖1. Metadata Refactory
+In Kylin 5.0, we have refactored the metadata storage structure and the
transaction process, removed the project lock and Epoch mechanism. This has
significantly improved transaction interface performance and system concurrency
capabilities.
+
+To upgrade from 5.0 alpha, beta, follow the [Metadata Migration
Guide](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/operations/system-operation/cli_tool/metadata_operation#migration)
+
+The metadata migration tool for upgrading from Kylin 4.0 is not tested, please
contact kylin user or dev mailing list for help.
+
+## Other Optimizations and Improvements
+Please refer to [Release Notes](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/release_notes/)
for more details.
+
+## Quick Start
+
+---
+
+### 🐳 Play Kylin in Docker
+
+To explore new features in Kylin 5 on a laptop, we recommend pulling the
Docker image and checking the [Apache Kylin Standalone Image on Docker
Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/apachekylin/apache-kylin-standalone) (For amd64
platform).
```shell
-./build/release/release.sh
+docker run -d \
+ --name Kylin5-Machine \
+ --hostname localhost \
+ -e TZ=UTC \
+ -m 10G \
+ -p 7070:7070 \
+ -p 8088:8088 \
+ -p 9870:9870 \
+ -p 8032:8032 \
+ -p 8042:8042 \
+ -p 2181:2181 \
+ apachekylin/apache-kylin-standalone:5.0.0-GA
```
+
+
+---
+### Introduction
+
+Kylin utilizes multidimensional modeling theory to build star or snowflake
schemas based on tables, making it a powerful tool for large-scale data
analysis. The **model** is Kylin's core component, consisting of three key
aspects: *model design*, *index design*, and *data loading*. By carefully
designing the model, optimizing indexes, and pre-computed data, queries
executed on Kylin can avoid scanning the entire dataset, potentially reducing
response times to mere seconds, even for petab [...]
+
++ **Model design** refers to establishing relationships between data tables to
enable fast extraction of key information from multidimensional data. The core
elements of model design are computed columns, dimensions, measures, and join
relations.
+
++ **Index design** refers to creating indexes (CUBEs) within the model to
precompute query results, thereby reducing query response time. Well-designed
indexes not only improve query performance but also help minimize the storage
and data-loading costs associated with precomputation.
+
++ **Data loading** refers to the process of importing data into the model,
enabling queries to utilize the pre-built indexes rather than scanning the
entire dataset. This allows for faster query responses by leveraging the
model's optimized structure.
+
+
+
+### Core Concepts
+
+- **Dimension**: A perspective of viewing data, which can be used to describe
object attributes or characteristics, for example, product category.
+
+- **Measure**: An aggregated sum, which is usually a continuous value, for
example, product sales.
+
+- **Pre-computation**: The process of aggregating data based on model
dimension combinations and of storing the results as indexes to accelerate data
query.
+
+- **Index**: Also called CUBE, which is used to accelerate data query. Indexes
are divided into:
+ - **Aggregate Index**: An aggregated combination of multiple dimensions
and measures, and can be used to answer aggregate queries such as total sales
for a given year.
+ - **Table Index**: A multilevel index in a wide table and can be used to
answer detailed queries such as the last 100 transactions of a certain user.
+
+
+### Why Use Kylin
+
++ **Low Query Latency vs. Large Volume**
+
+ When analyzing massive data, there are some techniques to speed up computing
and storage, but they cannot change the time complexity of query, that is,
query latency and data volume are linearly dependent.
+
+ If it takes 1 minute to query 100 million entries of data records, querying
10 billion data entries will take about 1 hour and 40 minutes. When companies
want to analyze all business data piled up over the years or to add complexity
to query, say, with more dimensions, queries will be running extremely slow or
even time out.
+
+ 
+
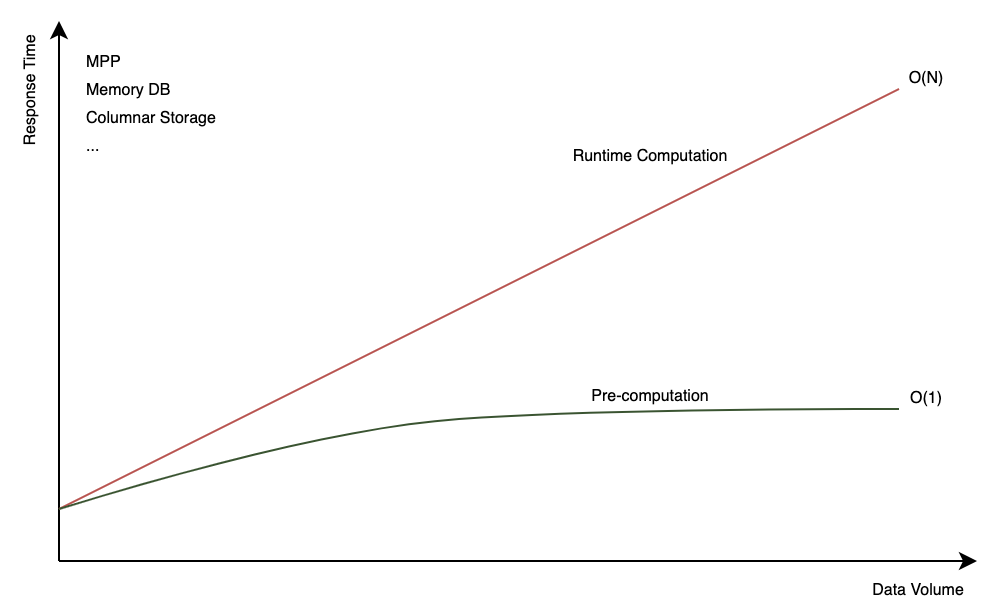
++ **Pre-computation vs. Runtime Computation**
+
+ Pre-computation and runtime computation are two approaches to calculating
results in data processing and analytics. **Pre-computation** involves
calculating and storing results in advance, so they can be quickly retrieved
when a query is run. In contrast, **runtime computation** dynamically computes
results during query execution, processing raw data and applying aggregations,
filters, or transformations as needed for each query.
+
+ Kylin primarily focuses on **pre-computation** to enhance query performance.
However, we also offer advanced features that partially support runtime
computation. For more details, please refer to [Table
Snapshot](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/model/snapshot/), [Runtime
Join](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/model/features/runtime_join), and [Internal
Table](https://kylin.apache.org/docs/internaltable/intro).
+
+
++ **Manual Modeling vs. Recommendation**
+
+ Before Kylin 5.0, model design had to be done manually, which was a tedious
process requiring extensive knowledge of multidimensional modeling. However,
this changed with the introduction of Kylin 5.0. We now offer a new approach to
model design, called **recommendation**, which allows models to be created by
importing SQL, along with an automatic way to remove unnecessary indexes.
Additionally, the system can leverage query history to generate index
recommendations, further optimizing [...]
+
+
++ **Batch Data vs. Streaming Data**
+
+ In the OLAP field, data has traditionally been processed in batches.
However, this is changing as more companies are now required to handle both
batch and streaming data to meet their business objectives. The ability to
process data in real-time has become increasingly critical for applications
such as real-time analytics, monitoring, and event-driven decision-making.
+
+ To address these evolving needs, we have introduced support for streaming
data in the new version. This allows users to efficiently process and analyze
data as it is generated, complementing the traditional batch processing
capabilities. For more details, please refer to [Streaming](streaming/intro.md).
