This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
kxiao pushed a commit to branch branch-2.0
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/doris.git
commit efc718c29cd103196abda4ca696766278dfd2041
Author: Luzhijing <82810928+luzhij...@users.noreply.github.com>
AuthorDate: Tue Jul 4 19:02:18 2023 +0800
[docs](releasenote) 2.0 beta release note (#21457)
---
README.md | 2 +-
docs/en/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md | 313 +++++++++++++++++++++++
docs/images/Beta_1.png | Bin 0 -> 54381 bytes
docs/images/Beta_2.png | Bin 0 -> 83910 bytes
docs/images/Beta_3.png | Bin 0 -> 137960 bytes
docs/images/Beta_4.png | Bin 0 -> 53043 bytes
docs/images/Beta_5.png | Bin 0 -> 53354 bytes
docs/images/Beta_6.png | Bin 0 -> 143116 bytes
docs/images/Beta_7.png | Bin 0 -> 93689 bytes
docs/images/Beta_8.png | Bin 0 -> 70644 bytes
docs/sidebars.json | 1 +
docs/zh-CN/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md | 303 ++++++++++++++++++++++
12 files changed, 618 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 781d249473..e9ac4e2890 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Apache Doris is an easy-to-use, high-performance and
real-time analytical databa
All this makes Apache Doris an ideal tool for scenarios including report
analysis, ad-hoc query, unified data warehouse, and data lake query
acceleration. On Apache Doris, users can build various applications, such as
user behavior analysis, AB test platform, log retrieval analysis, user portrait
analysis, and order analysis.
-🎉 Version 2.0.0 Alpha1 version released now. It is an alpha release that is
aimed to be used for evaluating the new features of Doris 2.0. It's recommended
to deploy 2.0.0 alpha1 version in a new test cluster for testing but **it
should not be deployed in production clusters**. Check out the 🔗[Release
Notes](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/releasenotes/release-2.0.0Alpha1)
here.
+🎉 Version 2.0-beta version released now. The 2.0 beta version already has a
better user experience in terms of functional integrity and system stability
than 2.0 Alpha. We welcome all users who have requirements for the new features
of the 2.0 version to deploy and upgrade. Check out the 🔗[Release
Notes](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta) here.
🎉 Version 1.2.5 released now! It is fully evolved release and all users are
encouraged to upgrade to this release. Check out the 🔗[Release
Notes](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/releasenotes/release-1.2.5) here.
diff --git a/docs/en/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
b/docs/en/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..adfe9abc9e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
@@ -0,0 +1,313 @@
+---
+{
+ "title": "Release 2.0-beta",
+ "language": "en"
+}
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+
+
+We are excited to announce the release of Apache Doris 2.0 Beta. We would like
to extend our heartfelt thanks to the 255 Apache Doris Contributors who have
committed over 3500 bug fixes and optimizations altogether. You are the driving
force behind all the new features and performance leap!
+
+> Download:
[https://doris.apache.org/download](https://doris.apache.org/download)
+>
+> GitHub source code:
[https://github.com/apache/doris/tree/branch-2.0](https://github.com/apache/doris/tree/branch-2.0)
+
+In the middle of 2023, we are half way on our roadmap and many steps closer to
our visions that we put forward on Doris Summit 2022:
+
+> We want to build Apache Doris into an all-in-one platform that can serve
most of our users' needs so as to maximize their productivity while inducing
the least development and maintainence costs. Specifically, it should be
capable of data analytics in multiple scenarios, support both online and
offline workloads, and deliver lightning performance in both high-throughput
interactive analysis and high-concurrency point queries. Also, in response to
industry trends, it should be able to p [...]
+
+Taking on these great visions means a path full of hurdles. We need to figure
out answers to all these difficult questions:
+
+- How to ensure real-time data writing without compromising query service
stability?
+- How to ensure online service continuity during data updates and table schema
changes?
+- How to store and analyze structured and semi-structured data efficiently in
one place?
+- How to handle multiple workloads (point queries, reporting, ad-hoc queries,
ETL/ELT, etc.) at the same time and guarantee isolation of them?
+- How to enable efficient execution of complicated SQLs, stability of big
queries, and observability of execution?
+- How to integrate and access data lakes and many heterogenous data sources
more easily?
+- How to improve query performance while largely reducing storage and
computation costs?
+
+We believe that life is miserable for either the developers or the users, so
we decided to tackle more challenges so that our users would suffer less. Now
we are happy to announce our progress with Apache Doris 2.0 Beta. These are
what you can expect from this new version:
+
+# A 10 times Performance Increase
+
+High performance is what our users identify us with. It has been repeatedly
proven by the test results of Apache Doris on ClickBench and TPC-H benchmarks
during the past year. But there remain some differences between benchmarking
and real-life application:
+
+- Benchmarking simplifies and abstracts real-world scenarios so it might not
cover the complex query statements that are frequently seen in data analytics.
+- Query statements in benchmarking are often fine-tuned, but in real life,
fine-tuning is just too demanding, exhausting, and time-consuming.
+
+That's why we introduced a brand new query optimizer: Nereids. With a richer
statistical base and the advanced Cascades framework, Nereids is capable of
self-tuning in most query scenarios, so users can expect high performance
without any fine-tuning or SQL rewriting. What's more, it supports all 99 SQLs
in TPC-DS.
+
+Testing on 22 TPC-H SQLs showed that Nereids, with no human intervention,
**brought an over 10-time performance increase compared to the old query
optimizer**. Similar results were reported by dozens of users who have tried
Apache Doris 2.0 Alpha in their business scenarios. It has really freed
engineers from the burden of fine-tuning.
+
+
+
+**Documentation**:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/query-acceleration/nereids/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/query-acceleration/nereids/)
+
+Nerieds is enabled by default in Apache Doris 2.0 Beta: `SET
enable_nereids_planner=true`.
+
+# Support for a Wider Range of Analytic Scenarios
+
+## A 10 times more cost-effective log analysis solution
+
+From a simple OLAP engine for real-time reporting to a data warehouse that is
capable of ETL/ELT and more, Apache Doris has been pushing its boundaries. With
version 2.0, we are making breakthroughs in log analysis.
+
+The common log analytic solutions within the industry are basically different
tradeoffs between high writing throughput, low storage cost, and fast text
retrieval. But Apache Doris 2.0 allows you to have them all. It has inverted
index that allows full-text searches on strings and equivalence/range queries
on numerics/datetime. Comparison tests with the same datasets in the same
hardware environment showed that Apache Doris was 4 times faster than
Elasticsearch in log data writing, 2 tim [...]
+
+
+
+We are also making advancements in multi-model data analysis. Apache Doris 2.0
supports two new data types: Map and Struct, as well as the quick writing,
functional analysis, and nesting of them.
+
+Read more:
[https://doris.apache.org/blog/Inverted%20Index](https://doris.apache.org/blog/Inverted%20Index)
+
+## High-concurrency data serving
+
+In scenarios such as e-commerce order queries and express tracking, there will
be a huge number of end data users inputing queries for a small piece of data
simultaneously. These are high-concurrency point queries, which can bring huge
pressure on the system. A traditional solution is to introduce Key-Value stores
like Apache HBase for such queries, and Redis as a cache layer to ease the
burden, but that means redundant storage and higher maintainence costs.
+
+For a column-oriented DBMS like Apache Doris, the I/O usage of point queries
will be multiplied. We need neater execution. Thus, we introduced row storage
format and row cache to increase row reading efficiency, short-circuit plans to
speed up data retrieval, and prepared statements to reduce frontend overheads.
+
+After these optimizations, Apache Doris 2.0 reached a concurrency level of
**30,000 QPS per node** on YCSB on a 16 Core 64G cloud server with 4×1T hard
drives, representing an improvement of **20 times** compared to older versions.
This makes Apache Doris a good alternative to HBase in high-concurrency
scenarios.
+
+
+
+Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/blog/High_concurrency](https://doris.apache.org/blog/High_concurrency)
+
+## Enhanced data lakehouse capabilities
+
+In Apache Doris 1.2, we introduced Multi-Catalog to support the auto-mapping
and auto-synchronization of data from heterogeneous sources. After
optimizations in data reading, execution engine, and query optimizer, Doris 1.2
delivered a 3~5 times faster query performance than Presto/Trino in standard
tests.
+
+In Apache Doris 2.0, we extended the list of data sources supported and
conducted optimizations according to the actual production environment of users.
+
+- More data sources supported
+ - Supported snapshot queries on Hudi Copy-on-Write tables and read optimized
queries on Hudi Merge-on-Read tables; The support for incremental queries and
snapshot queries on Merge-on-Read tables is under plan.
+ - Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hudi/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hudi/)
+ - Supported connection to Oceanbase via JDBC Catalog, prolonging the list of
supported relational databases which include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle,
SQLServer, Doris, ClickHouse, SAP HANA, and Trino/Presto.
+ - Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/jdbc/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/jdbc/)
+- Data Privilege Control
+ - Supported authorization for Hive Catalog via Apache Range; Supported
extensible privilege authorization plug-ins to allow user-defined authorization
method on any catalog.
+ - Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hive/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hive/)
+- Performance improvement
+ - Accelerated reading of flat tables and large numbers of small files;
improved query speed by dozens of times; reduced reading overhead by techniques
such as full loading of small files, I/O coalescing, and data pre-fetching.
+ - Increased query speed on ORC/Parquet files by 100% compared to version 1.2.
+ - 
+
+ - Supported local caching of lakehouse data. Users can cache data from HDFS
or object storage in local disks to speed up queries involving the same data.
In the case of cache hits, querying lakehouse data will be as quick as querying
internal data in Apache Doris.
+ - Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/filecache/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/filecache/)
+ - Supported collection of external table statistics. Users can obtain
statistics about their specified external tables via the Analyze statement so
that Nereids can fine-tune the query plan for complicated SQLs more
efficiently.
+ - Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/)
+ - Improved data writeback speed of JDBC Catalog. By way of PrepareStmt and
other batch methods, users can write data back to relational databases such as
MySQL and Oracle via the INSERT INTO command much faster.
+ - 
+
+ -
+
+# A Unified Platform for Multiple Analytic Workloads
+
+## A self-adaptive parallel execution model
+
+With the expansion of user base, Apache Doris is undertaking more and more
analytic workloads while handling larger and larger data sizes. A big challenge
is to ensure high execution efficiency for all these workloads and avoid
resource preemption.
+
+Older versions of Apache Doris had a volcano-based execution engine. To give
full play to all the machines and cores, users had to set the execution
concurrency themselves (for example, change
`parallel_fragment_exec_instance_num` from the default value 1 to 8 or 16). But
problems existed when Doris had to deal with multiple queries at the same time:
+
+- Instance operators took up the threads and the query tasks didn't get
executed. Logical deadlocks occurred.
+- Instance threads were scheduled by a system scheduling mechanism and the
switching between threads brought extra overheads.
+- When processing various analytic workloads, instance threads might fight for
CPU resources so queries and tenants might interrupt each other.
+
+Apache 2.0 brought in a Pipeline execution engine to solve these problems. In
this engine, the execution of queries are driven by data. The blocking
operators in all the query execution processes are split into pipelines.
Whether a pipeline gets an execution thread depends on whether its data is
ready. As a result:
+
+- The Pipeline execution model splits the query execution plan into pipeline
tasks based on the blocking logic and asynchronizes the blocking operations, so
no instance is going to take up a single thread for a long time.
+- It allows users to manage system resources more flexibly. They can take
different scheduling strategies to assign CPU resources to various queries and
tenants.
+- It also pools data from all buckets, so the number of instances will not be
limited by the number of buckets, and the system doesn't have to frequently
create and destroy threads.
+
+With the Pipeline execution engine, Apache Doris is going to offer **faster
queries and higher stability in hybrid workload scenarios**.
+
+Doc:[
https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/query-acceleration/pipeline-execution-engine/](
https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/query-acceleration/pipeline-execution-engine/)
+
+The Pipeline execution engine is enabled by default in Apache Doris 2.0: `Set
enable_pipeline_engine = true`. `parallel_pipeline_task_num` represents the
number of pipeline tasks that are parallelly executed in SQL queries. The
default value of it is `0`, and users can change the value as they need. For
those who are upgrading to Apache Doris 2.0 from an older version, it is
recommended to set the value of `parallel_pipeline_task_num` to that of
`parallel_fragment_exec_instance_num` in t [...]
+
+## Workload management
+
+Based on the Pipeline execution engine, Apache Doris 2.0 divides the workloads
into Workload Groups for fine-grained management of memory and CPU resources.
+
+By relating a query to a Workload Group, users can limit the percentage of
memory and CPU resources used by one query on the backend nodes and configure
memory soft limits for resource groups. When there is a cluster resource
shortage, the system will kill the largest memory-consuming tasks; when there
is sufficient cluster resources, once the Workload Groups use more resources
than expected, the idle cluster resources will be shared among multiple
Workload Groups and the system memory w [...]
+
+```SQL
+create workload group if not exists etl_group
+properties (
+ "cpu_share"="10",
+ "memory_limit"="30%",
+ "max_concurrency" = "10",
+ "max_queue_size" = "20",
+ "queue_timeout" = "3000"
+);
+```
+
+You can check the existing Workload Group via the `Show` command:
+
+
+
+## Query queue
+
+When creating a Workload Group, users can set a maximum query number for it.
Queries beyond that limit will wait for execution in the query queue.
+
+- `max_concurrency`: the maximum number of queries allowed by the current
Workload Group
+- `max_queue_size`: the length of query queue. After all spots are filled, any
new queries will be rejected.
+- `queue_timeout`: the waiting time of a query in a queue, measured in
miliseconds. If a queue has been waiting for longer than this limit, it will be
rejected.
+
+
+
+Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/admin-manual/workload-group/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/admin-manual/workload-group/)
+
+# Elastic Scaling and Storage-Compute Separation
+
+When it comes to computation and storage resources, what do users want?
+
+- **Elastic scaling of computation resources**: Scale up resources quickly in
peak times to increase efficiency and scale down in valley times to reduce
costs.
+- **Lower storage costs**: Use low-cost storage media and separate storage
from computation.
+- **Separation of workloads**: Isolate the computation resources of different
workloads to avoid preemption.
+- **Unified management of data**: Simply manage catalogs and data in one place.
+
+To separate storage and computation is a way to realize elastic scaling of
resources, but it demands more efforts in maintaining storage stability, which
determines the stability and continuity of OLAP services. To ensure storage
stability, we introduced mechanisms including cache management, computation
resource management, and garbage collection.
+
+ In this respect, we divide our users into three groups after investigation:
+
+1. Users with no need for resource scaling
+2. Users requiring resource scaling, low storage costs, and workload
separation from Apache Doris
+3. Users who already have a stable large-scale storage system and thus require
an advanced compute-storage-separated architecture for efficient resource
scaling
+
+Apache Doris 2.0 provides two solutions to address the needs of the first two
types of users.
+
+1. **Compute nodes**. We introduced stateless compute nodes in version 2.0.
Unlike the mix nodes, the compute nodes do not save any data and are not
involved in workload balancing of data tablets during cluster scaling. Thus,
they are able to quickly join the cluster and share the computing pressure
during peak times. In addition, in data lakehouse analysis, these nodes will be
the first ones to execute queries on remote storage (HDFS/S3) so there will be
no resource competition between [...]
+ 1. Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/advanced/compute_node/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/advanced/compute_node/)
+2. **Hot-cold data separation**. Hot/cold data refers to data that is
frequently/seldom accessed, respectively. Generally, it makes more sense to
store cold data in low-cost storage. Older versions of Apache Doris support
lifecycle management of table partitions: As hot data cooled down, it would be
moved from SSD to HDD. However, data was stored with multiple replicas on HDD,
which was still a waste. Now, in Apache Doris 2.0, cold data can be stored in
object storage, which is even chea [...]
+ 1. Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/advanced/cold_hot_separation/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/advanced/cold_hot_separation/)
+
+ 2. Read more:
[https://doris.apache.org/blog/HCDS/](https://doris.apache.org/blog/HCDS/)
+
+
+
+For the third type of users, the SelectDB team is going to contribute the
SelectDB Cloud Compute-Storage-Separation solution to the Apache Doris project.
The performance and stability of this solution has stood the test of hundreds
of companies in their production environment. The merging of the solution to
Apache Doris is underway.
+
+# Faster, Stabler, and Smarter Data Writing
+
+## Higher speed in data writing
+
+As part of our continuing effort to strengthen the real-time analytic
capability of Apache Doris, we have improved the end-to-end real-time data
writing of version 2.0:
+
+- When tested with the TPC-H 100G standard dataset, Apache Doris 2.0 reached a
data loading speed of over 550MB/s for a single node with its `insert into
select` method, which was a **200% increase**. In triple-replica import of 144G
data, it delivered a single-node data loading speed of 121MB/s via the Stream
Load method, **up 400%** in system throughput.
+- We have introduced single-replica data loading into version 2.0. Apache
Doris guarantees high data reliability and system availability by its
multi-replica mechanism, but multi-replica writing also multiplies the CPU and
memory usage. Now Apache Doris only writes one data copy to the memory, and
then it synchronizes the storage file to other copies, so it can save a lot of
the computation resources. In large data ingestion, the single-replica loading
method can accelerate data ingestio [...]
+
+## Greater stability in high-concurrency data writing
+
+The merging of small files, write amplification, and the consequential disk
I/O and CPU overheads are often the sources of system instability. Hence, we
introduced Vertical Compaction and Segment Compaction in version 2.0 to
eliminate OOM errors in compaction and avoid the generation of too many segment
files during data writing. After such improvements, Apache Doris can write data
50% faster while using only 10% of the memory that it previously used.
+
+Read more:
[https://doris.apache.org/blog/Compaction](https://doris.apache.org/blog/Compaction)
+
+## Auto-synchronization of table schema
+
+The latest Flink-Doris-Connector allows users to synchronize the whole
database (such as MySQL) to Apache Doris by one simple step. According to our
test results, one single synchronization task can undertake the real-time
concurrent writing of thousands of tables. Apache Doris has automated the
updating of upstream table schema and data so users no longer need to go
through a complicated synchronization procedure. Also, changes in the upstream
data schema will be automatically captured [...]
+
+# Support for Partial Column Update in the Unique Key Model
+
+Apache Doris 1.2 realized real-time writing and quick query execution at the
same time with the Merge-on-Write mechanism in the Unique Key Model. Now in
version 2.0, we have further improved the Unique Key Model. It supports partial
column update so when ingesting multiple source tables, users don't have to
merge them into one flat table in advance.
+
+On this basis, we have also enhanced the capability of Merge-on-Write. Apache
Doris 2.0 is 50% faster than Apache Doris 1.2 in large data writing and 10
times faster in high-concurrency data writing. A parallel processing mechanism
is available to avoid "publish timeout" (E-3115), and a more efficient
compaction mechanism is in place to prevent "too many versions" (E-235). All
this allows users to replace Merge-on-Read with Merge-on-Write in more
scenarios. Plus, partial column update ma [...]
+
+The execution of partial column update is simple.
+
+**Example (Stream Load):**
+
+Suppose that you have the following table schema:
+
+```Python
+mysql> desc user_profile;
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+| id | INT | Yes | true | NULL | |
+| name | VARCHAR(10) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| age | INT | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| city | VARCHAR(10) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| balance | DECIMALV3(9, 0) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| last_access_time | DATETIME | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+```
+
+If you need to batch update the "balance" and "last access time" fields for
the last 10 seconds, you can put the updates in a CSV file as follows:
+
+```Python
+1,500,2023-07-03 12:00:01
+3,23,2023-07-03 12:00:02
+18,9999999,2023-07-03 12:00:03
+```
+
+Then, add a header `partial_columns:true` and specify the relevant column
names in the the Stream Load command:
+
+```Python
+curl --location-trusted -u root: -H "partial_columns:true" -H
"column_separator:," -H "columns:id,balance,last_access_time" -T /tmp/test.csv
http://127.0.0.1:48037/api/db1/user_profile/_stream_load
+```
+
+# Farewell to OOM
+
+Memory management might not be on the priority list of users until there is a
memory problem. However, real-life analytics is full of extreme cases that are
challenging memory stability. In large computation tasks, OOM errors often
cause queries to fail or even result in a backend downtime.
+
+To solve this, we have improved the memory data structures, reconstructed the
MemTrackers, and introduced soft memory limits for queries and a GC mechansim
to cope with process memory overflow. The new memory management mechanism
allocates, caculates, and monitors memory more efficiently. According to
benchmark tests, pressure tests, and user feedback, it eliminates most memory
hotspots and backend downtime. Even if there is an OOM error, users can locate
the question spot based on the l [...]
+
+In a word, Apache Doris 2.0 is able to handle complicated computation and
large ETL/ELT operations with greater system stability.
+
+Read more:
[https://doris.apache.org/blog/Memory_Management/](https://doris.apache.org/blog/Memory_Management/)
+
+# Support for Kubernetes Deployment
+
+Older versions of Apache Doris communicate based on IP, so any host failure in
Kubernetes deployment that causes a POD IP drift will lead to cluster
unavailability. Now, version 2.0 supports FQDN. That means the failed Doris
nodes can recover automatically without human intervention, which lays the
foundation for Kubernetes deployment and elastic scaling.
+
+Doc:
[https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/install/k8s-deploy/](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/install/k8s-deploy/)
+
+# Support for Cross-Cluster Replication
+
+For data synchronization across multiple clusters, Apache Doris used to
require regular data backup and restoration via the Backup/Restore command. The
process required intermediate storage and came with high latency. Apache Doris
2.0 Beta supports cross-cluster replication (CCR), which automates this
process. Data changes at the database/table level in the source cluster will be
synchronized to the target cluster. This feature allows for higher availability
of data, read/write workload [...]
+
+# Behavior Change
+
+- 1.2-lts can be scrolled and upgraded to 2.0-beta, while 2.0-alpha can be
shut down and upgraded to 2.0-beta
+- Query optimizer switch default on ` enable_ Nereids_ Planner=true `;
+- Non vectorized code has been removed from the system, so 'enable'_
Vectorized_ The 'engine' parameter will no longer be effective;
+- Add Parameter ` enable_ Single_ Replica_ Compaction `;
+- By default, use datev2, datetimev2, and decimalv3 to create tables, but do
not support creating tables with datev1, datetimev1, and decimalv2;
+- Decimalv3 is used by default in JDBC and Iceberg Catalog;
+- Add AGG for date type_ State;
+- Remove the cluster column from the backend table;
+- For better compatibility with BI tools, when displaying create tables,
display date v2 and date timev2 as date and date time.
+- Added max in BE startup script_ Check for openfiles and swap, so if the
system configuration is not reasonable, be may fail to start;
+- Prohibit logging in without a password when accessing FE from localhost;
+- When there is a Multi Catalog in the system, querying the information schema
only displays data from the internal catalog by default;
+- Limited the depth of the expression tree, defaulting to 200;
+- The array string returns a single quotation mark to a double quotation mark;
+- Rename Doris' process names to DorisFE and DorisBE;
+
+# Apache Doris 2.0 GA is just around the corner!
+
+During the recent one and a half months after Apache Doris 2.0 Alpha was
released, we have been honing the key features and perfectionating Doris
according to the test feedback from our hundreds of enterprise users. Now,
Apache Doris 2.0 Beta is more mature and stable, and will surely provide better
user experience.
+
+If you have any questions when investigating, testing, and deploying Apache
Doris, please find us on [Slack](https://t.co/ZxJuNJHXb2). Our developers will
be happy to provide targeted support.
+
+In addition to the foregoing functionality, some new features are undergoing
the final debugging and will be available in Apache Doris 2.0.0 GA and the
subsequent versions, including multi-table materialized view, expression
support in single-table materialized view, dynamic schema table, and Doris
binlog. We will keep you informed of our progress.
+
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_1.png b/docs/images/Beta_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0c2e4bee61
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_1.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_2.png b/docs/images/Beta_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c34b69fef8
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_2.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_3.png b/docs/images/Beta_3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..903d8aaf20
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_3.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_4.png b/docs/images/Beta_4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..50989fef2c
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_4.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_5.png b/docs/images/Beta_5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a899f37dd7
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_5.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_6.png b/docs/images/Beta_6.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..586d9681b2
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_6.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_7.png b/docs/images/Beta_7.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..367ad94997
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_7.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/Beta_8.png b/docs/images/Beta_8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ff41ac379f
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/Beta_8.png differ
diff --git a/docs/sidebars.json b/docs/sidebars.json
index f055ab4b20..4e31a3fd91 100644
--- a/docs/sidebars.json
+++ b/docs/sidebars.json
@@ -1244,6 +1244,7 @@
"type": "category",
"label": "Release notes",
"items": [
+ "releasenotes/release-2.0-beta",
"releasenotes/release-2.0.0Alpha1",
"releasenotes/release-1.2.5",
"releasenotes/release-1.2.4.1",
diff --git a/docs/zh-CN/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
b/docs/zh-CN/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..332138923e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/zh-CN/docs/releasenotes/release-2.0-beta.md
@@ -0,0 +1,303 @@
+---
+{
+ "title": "Release 2.0-beta",
+ "language": "zh-CN"
+}
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+亲爱的社区小伙伴们,我们很高兴地向大家宣布,Apache Doris 2.0-beta 版本已于 2023 年 7 月 3 日正式发布!**在
2.0-beta 版本中有超过 255 位贡献者为 Apache Doris 提交了超过 3500 个优化与修复**,欢迎大家下载使用!
+
+> 下载链接:[https://doris.apache.org/download](https://doris.apache.org/download)
+>
+> GitHub
源码:[https://github.com/apache/doris/tree/branch-2.0](https://github.com/apache/doris/tree/branch-2.0)
+
+
+在今年年初举办的 Doris Summit 年度峰会上,我们曾发布了 Apache Doris 的 2023 年 Roadmap 并提出了新的愿景:
+
+> 我们希望用户可以基于 Apache Doris
构建多种不同场景的数据分析服务、同时支撑在线与离线的业务负载、高吞吐的交互式分析与高并发的点查询;通过一套架构实现湖和仓的统一、在数据湖和多种异构存储之上提供无缝且极速的分析服务;也可通过对日志/文本等半结构化乃至非结构化的多模数据进行统一管理和分析、来满足更多样化数据分析的需求。
+>
+> 这是我们希望 Apache Doris
能够带给用户的价值,**不再让用户在多套系统之间权衡,仅通过一个系统解决绝大部分问题,降低复杂技术栈带来的开发、运维和使用成本,最大化提升生产力。**
+
+面对海量数据的实时分析难题,这一愿景的实现无疑需要克服许多困难,尤其是在应对实际业务场景的真实诉求中更是遭遇了许多挑战:
+
+- 如何保证上游数据实时高频写入的同时保证用户的查询稳定;
+- 如何在上游数据更新及表结构变更的同时保证在线服务的连续性;
+- 如何实现结构化与半结构化数据的统一存储与高效分析;
+- 如何同时应对点查询、报表分析、即席查询、ETL/ELT 等不同的查询负载且保证负载间相互隔离?
+- 如何保证复杂 SQL 语句执行的高效性、大查询的稳定性以及执行过程的可观测性?
+- 如何更便捷地集成与访问数据湖以及各种异构数据源?
+- 如何在大幅降低数据存储和计算资源成本的同时兼顾高性能查询?
+- ……
+
+秉持着“**将易用性留给用户、将复杂性留给自己**”的原则,为了克服以上一系列挑战,从理论基础到工程实现、从理想业务场景到极端异常
Case、从内部测试通过到大规模生产可用,我们耗费了更多的时间与精力在功能的开发、验证、持续迭代与精益求精上。值得庆祝的是,在经过近半年的开发、测试与稳定性调优后,Apache
Doris 终于迎来了 2.0-beta 版本的正式发布!而这一版本的成功发布也使得我们的愿景离现实更进一步!
+
+
+
+
+# 盲测性能 10 倍以上提升!
+
+## 全新查询优化器
+
+高性能是 Apache Doris 不断追求的目标。过去一年在 Clickbench、TPC-H
等公开测试数据集上的优异表现,已经证明了其在执行层以及算子优化方面做到了业界领先,但从 Benchmark 到真实业务场景之间还存在一定距离:
+
+- Benchmark 更多是真实业务场景的抽象、提炼与简化,而现实场景往往可能面临更复杂的查询语句,这是测试所无法覆盖的;
+- Benchmark 查询语句可枚举、可针对性进行调优,而真实业务场景的调优极度依赖工程师的心智成本、调优效率往往较为低下且过于消耗工程师人力;
+
+基于此,我们着手研发了现代架构的全新查询优化器,并在 Apache Doris 2.0-beta 版本全面启用。全新查询优化器采取了更先进的
Cascades 框架、使用了更丰富的统计信息、实现了更智能化的自适应调优,在绝大多数场景无需任何调优和 SQL 改写即可实现极致的查询性能,同时对复杂
SQL 支持得更加完备、可完整支持 TPC-DS 全部 99 个 SQL。
+
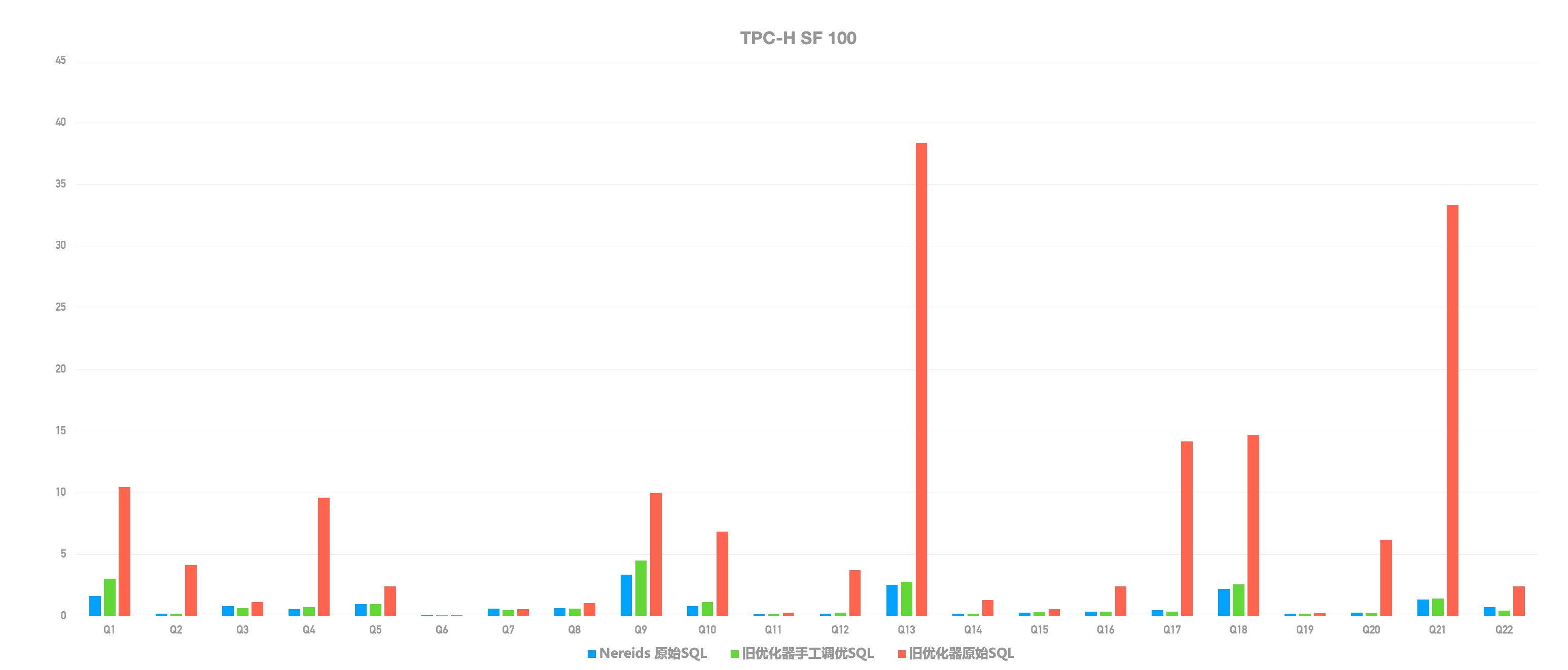
+我们对全新查询优化器的执行性能进行了盲测,仅以 TPC-H 22 个 SQL 为例 ,**全新优化器在未进行任何手工调优和 SQL 改写的情况下**
**查询耗时**,盲测性能提升了超过 10 倍!而在数十个 2.0 版本用户的真实业务场景中,绝大多数原始 SQL
执行效率得以极大提升,真正解决了人工调优的痛点!
+
+
+
+参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/nereids](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/nereids)
+
+如何开启:`SET enable_nereids_planner=true` 在 Apache Doris 2.0-beta 版本中全新查询优化器已经默认开启
+
+## 自适应的并行执行模型
+
+过去 Apache Doris 的执行引擎是基于传统的火山模型构建,为了更好利用多机多核的并发能力,过去我们需要手动设置执行并发度(例如将
`parallel_fragment_exec_instance_num` 这一参数从默认值 1 手工设置为 8 或者
16),在存在大量查询任务时存在一系列问题:
+
+- 大查询、小查询需要设置不同的instance 并发度,系统不能做到自适应调整;
+- Instance 算子占用线程阻塞执行,大量查询任务将导致执行线程池被占满、无法响应后续请求,甚至出现逻辑死锁;
+- Instance 线程间的调度依赖于系统调度机制,线程进行反复切换将产生额外的性能开销;
+- 在不同分析负载并存时,Instance 线程间可能出现 CPU 资源争抢的情况,可能导致大小查询、不同租户之间相互受影响;
+
+针对以上问题,Apache Doris 2.0 引入了 Pipeline 执行模型作为查询执行引擎。在 Pipeline
执行引擎中,**查询的执行是由数据来驱动控制流变化的,** 各个查询执行过程之中的阻塞算子被拆分成不同 Pipeline,各个 Pipeline
能否获取执行线程调度执行取决于前置数据是否就绪,因此实现了以下效果:
+
+- Pipeline 执行模型通过阻塞逻辑将执行计划拆解成 Pipeline Task,将 Pipeline Task
分时调度到线程池中,实现了阻塞操作的异步化,解决了 Instance 长期占用单一线程的问题。
+- 可以采用不同的调度策略,实现 CPU 资源在大小查询间、不同租户间的分配,从而更加灵活地管理系统资源。
+- Pipeline 执行模型还采用了数据池化技术,将单个数据分桶中的数据进行池化,从而解除分桶数对 Instance 数量的限制,提高 Apache
Doris 对多核系统的利用能力,同时避免了线程频繁创建和销毁的问题。
+
+通过 Pipeline 执行引擎,**Apache Doris 在混合负载场景中的查询性能和稳定性都得以进一步提升**。
+
+参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/pipeline-execution-engine](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/pipeline-execution-engine)
+
+如何开启:` Set enable_pipeline_engine = true `该功能在 Apache Doris 2.0 版本中将默认开启,BE
在进行查询执行时默认将 SQL 的执行模型转变 Pipeline 的执行方式。`parallel_pipeline_task_num`代表了 SQL
查询进行查询并发的 Pipeline Task 数目。Apache Doris 默认配置为`0`,此时 Apache Doris 会自动感知每个 BE 的
CPU 核数并把并发度设置为 CPU
核数的一半,用户也可以实际根据自己的实际情况进行调整。对于从老版本升级的用户,建议用户将该参数设置成老版本中`parallel_fragment_exec_instance_num`的值。
+
+# 查询稳定性进一步提升
+
+## 多业务资源隔离
+
+随着用户规模的极速扩张,越来越多的用户将 Apache Doris 用于构建企业内部的统一分析平台。这一方面需要 Apache Doris
去承担更大规模的数据处理和分析,另一方面也需要 Apache Doris
同时去应对更多分析负载的挑战,而其中的关键在于如何保证不同负载能够在一个系统中稳定运行。
+
+Apache Doris 2.0 版本中基于 Pipeline 执行引擎增加了 Workload 管理器 ,通过对 Workload
进行分组管理,以保证内存和 CPU 资源的精细化管控。
+
+在过去版本中 Apache Doris 通过资源标签的方式进行了多租户资源隔离,可以通过节点资源划分来避免不同业务间的相互干扰,而 Workload
Group 实现了更精细化的资源管控方式,通过将 Query 与 Workload Group 相关联,可以限制单个 Query 在 BE 节点上的 CPU
和内存资源的百分比,并可以配置开启资源组的内存软限制。当集群资源紧张时,将自动 Kill
组内占用内存最大的若干个查询任务以减缓集群压力。当集群资源空闲时,一旦 Workload Group 使用资源超过预设值时,多个 Workload
将共享集群可用空闲资源并自动突破阙值,继续使用系统内存以保证查询任务的稳定执行。
+
+```
+create workload group if not exists etl_group
+properties (
+ "cpu_share"="10",
+ "memory_limit"="30%",
+ "max_concurrency" = "10",
+ "max_queue_size" = "20",
+ "queue_timeout" = "3000"
+);
+```
+
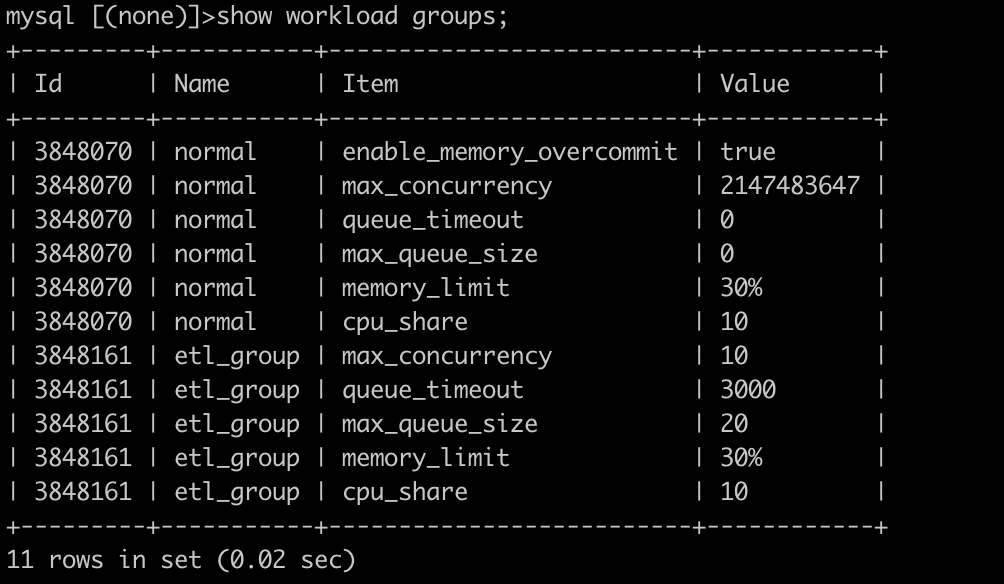
+可以通过 `Show` 命令来查看创建的 Workload Group,例如:
+
+
+
+## 作业排队
+
+同时在 Workload Group 中我们还引入了查询排队的功能,在创建 Workload Group
时可以设置最大查询数,超出最大并发的查询将会进行队列中等待执行。
+
+- `max_concurrency` 当前 Group允许的最大查询数,超过最大并发的查询到来时会进入排队逻辑;
+- `max_queue_size`查询排队的长度,当队列满了之后,新来的查询会被拒绝;
+- `queue_timeout`查询在队列中等待的时间,如果查询等待时间超过等待时间查询将会被拒绝,时间单位为毫秒;
+
+
+
+参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/admin-manual/workload-group/](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/admin-manual/workload-group/)
+
+## 彻底告别 OOM
+
+在内存充足时内存管理通常对用户是无感的,但真实场景中往往面临着各式各样的极端
Case,这些都将为内存性能和稳定性带来挑战,尤其是在面临内存资源消耗巨大的复杂计算和大规模作业时,由于内存 OOM 导致查询失败甚至可能造成 BE 进程宕机。
+
+因此我们逐渐统一内存数据结构、重构 MemTracker、开始支持查询内存软限,并引入进程内存超限后的 GC 机制,同时优化了高并发的查询性能等。在 2.0
版本中我们引入了全新的内存管理框架,通过有效的内存分配、统计、管控,在 Benchmark、压力测试和真实用户业务场景的反馈中,基本消除了内存热点以及 OOM
导致 BE 宕机的问题,即使发生 OOM
通常也可依据日志定位内存位置并针对性调优,从而让集群恢复稳定,对查询和导入的内存限制也更加灵活,在内存充足时让用户无需感知内存使用。
+
+通过以上一系列优化,Apache Doris 2.0 版本在应对复杂计算以及大规模 ETL/ELT 操作时,内存资源得以有效控制,系统稳定性表现更上一个台阶。
+
+详细介绍:[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Z5N-uZrFE3Qhn5zTyEDomQ](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Z5N-uZrFE3Qhn5zTyEDomQ)
+
+# 高效稳定的数据写入
+
+## 更高的实时数据写入效率
+
+### 导入性能进一步提升
+
+聚焦于实时分析,我们在过去的几个版本中在不断增强实时分析能力,其中端到端的数据实时写入能力是优化的重要方向,在 Apache Doris 2.0
版本中,我们进一步强化了这一能力。通过 Memtable 不使用 Skiplist、并行下刷、单副本导入等优化,使得导入性能有了大幅提升:
+
+- 使用 Stream Load 对 TPC-H 144G lineitem表 原始数据进行三副本导入 48 bucket 明细表,吞吐量提升 100%。
+- 使用 Stream Load 对 TPC-H 144G lineitem表 原始数据进行三副本导入 48 bucket Unique Key
表,吞吐量提升 200%。
+- 对 TPC-H 144G lineitem 表进行 insert into select 导入 48 bucket Duplicate
明细表,吞吐量提升 50%。
+- 对 TPC-H 144G lineitem 表进行 insert into select 导入 48 bucket UniqueKey 表,吞吐提升
150%。
+
+### 数据高频写入更稳定
+
+在高频数据写入过程中,小文件合并和写放大问题以及随之而来的磁盘 I/O和 CPU 资源开销是制约系统稳定性的关键,因此在 2.0 版本中我们引入了
Vertical Compaction 以及 Segment Compaction,用以彻底解决 Compaction 内存问题以及写入过程中的
Segment 文件过多问题,资源消耗降低 90%,速度提升 50%,**内存占用仅为原先的 10%。**
+
+详细介绍:[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BqiMXRJ2sh4jxKdJyEgM4A](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BqiMXRJ2sh4jxKdJyEgM4A)
+
+### 数据表结构自动同步
+
+在过去版本中我们引入了毫秒级别的 Schema Change,而在最新版本 Flink-Doris-Connector 中,我们实现了从 MySQL
等关系型数据库到 Apache Doris
的一键整库同步。在实际测试中单个同步任务可以承载数千张表的实时并行写入,从此彻底告别过去繁琐复杂的同步流程,通过简单命令即可实现上游业务数据库的表结构及数据同步。同时当上游数据结构发生变更时,也可以自动捕获
Schema 变更并将 DDL 动态同步到 Doris 中,保证业务的无缝运行。
+
+详细介绍:[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ur4VpJtjByVL0qQNy_iQBw](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ur4VpJtjByVL0qQNy_iQBw)
+
+## 主键模型支持部分列更新
+
+在 Apache Doris 1.2 版本中我们引入了 Unique Key 模型的 Merg-on-Write
写时合并模式,在上游数据高频写入和更新的同时可以保证下游业务的高效稳定查询,实现了**实时写入和极速查询的统一。** 而 2.0 版本我们对 Unique
Key 模型进行了全面增强。在功能上,支持了新的部分列更新能力,在上游多个源表同时写入时无需提前处理成宽表,直接通过部分列更新在写时完成
Join,大幅简化了宽表的写入流程。
+
+在性能上,2.0 版本大幅增强了 Unique Key 模型 Merge-on-Write 的大数据量写入性能和并发写入能力,大数据量导入较 1.2
版本有超过 50% 的性能提升,高并发导入有超过 10 倍的性能提升,并通过高效的并发处理机制来彻底解决了 publish timeout(Error
-3115) 问题,同时由于 Doris 2.0 高效的 Compaction 机制,也不会出现 too many versions (Error-235)
问题。这使得 Merge-on-Write 能够在更广泛的场景下替代 Merge-on-Read 实现,同时我们还利用部分列更新能力来降低 UPDATE
语句和 DELETE 语句的计算成本,整体性能提升约 50%。
+
+### 部分列更新的使用示例(Stream Load):
+
+例如有表结构如下
+
+```
+mysql> desc user_profile;
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+| id | INT | Yes | true | NULL | |
+| name | VARCHAR(10) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| age | INT | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| city | VARCHAR(10) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| balance | DECIMALV3(9, 0) | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
+| last_access_time | DATETIME | Yes | false | NULL | NONE |
++------------------+-----------------+------+-------+---------+-------+
+```
+
+用户希望批量更新最近 10s 发生变化的用户的余额和访问时间,可以把数据组织在如下 csv 文件中
+
+```
+1,500,2023-07-03 12:00:01
+3,23,2023-07-03 12:00:02
+18,9999999,2023-07-03 12:00:03
+```
+
+然后通过 Stream Load,增加 Header `partial_columns:true`,并指定要导入的列名即可完成更新
+
+```
+curl --location-trusted -u root: -H "partial_columns:true" -H
"column_separator:," -H "columns:id,balance,last_access_time" -T /tmp/test.csv
http://127.0.0.1:48037/api/db1/user_profile/_stream_load
+```
+
+# 更广泛的分析场景支持
+
+## 10 倍以上性价比的日志分析方案
+
+从过去的实时报表和 Ad-hoc 等典型 OLAP 场景到 ELT/ETL、日志检索与分析等更多业务场景,Apache Doris
正在不断拓展应用场景的边界,而日志数据的统一存储与分析正是我们在 2.0 版本的重要突破。
+
+过去业界典型的日志存储分析架构难以同时兼顾 高吞吐实时写入、低成本大规模存储与高性能文本检索分析,只能在某一方面或某几方面做权衡取舍。而在 Apache
Doris 2.0
版本中,我们引入了全新倒排索引、以满足字符串类型的全文检索和普通数值/日期等类型的等值、范围检索,同时进一步优化倒排索引的查询性能、使其更加契合日志数据分析的场景需求,同时结合过去在大规模数据写入和低成本存储等方面的优势,实现了更高性价比的日志分析方案。
+
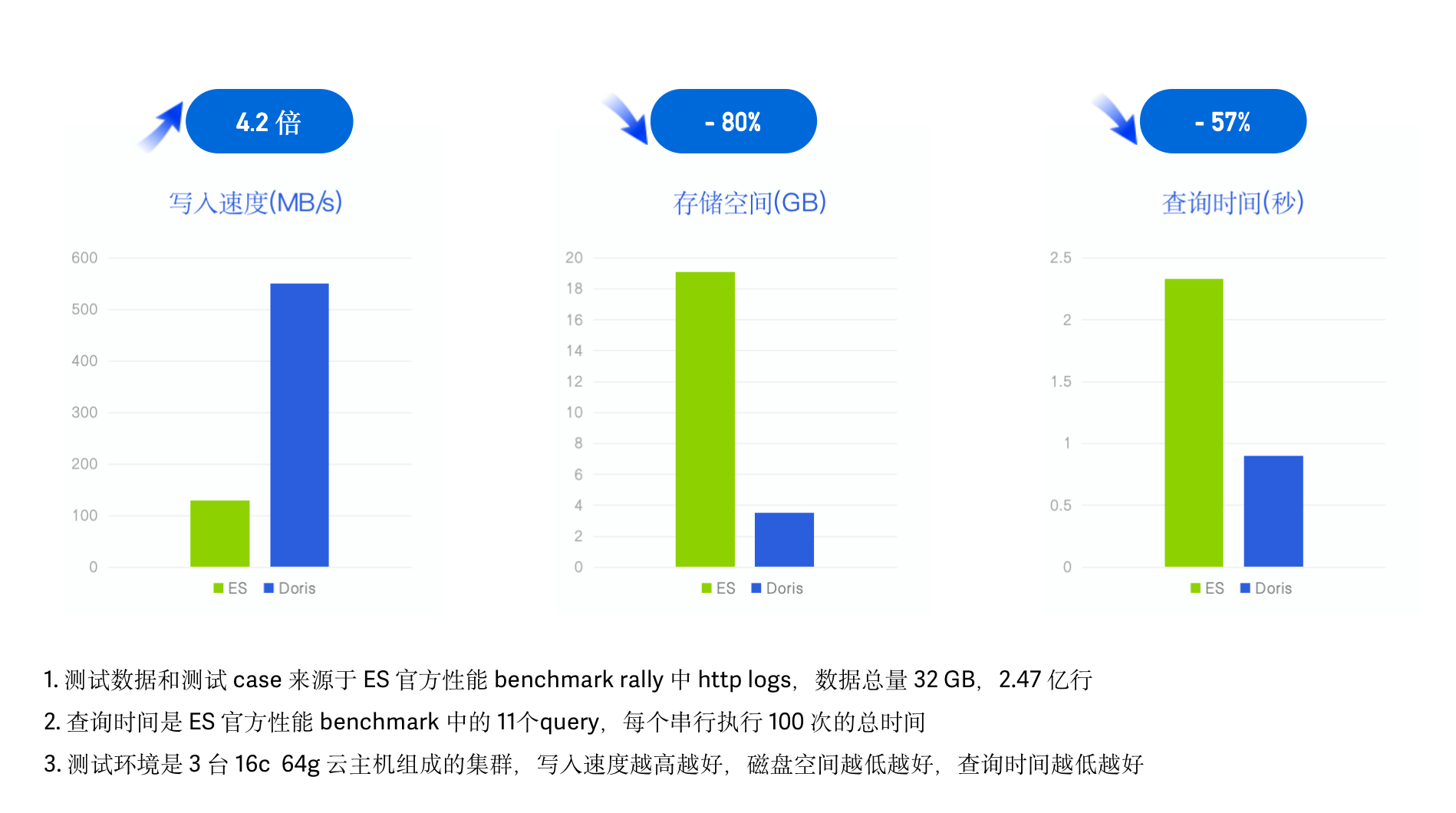
+在相同硬件配置和数据集的测试表现上,Apache Doris 相对于 ElasticSearch 实现了日志数据写入速度提升 4 倍、存储空间降低
80%、查询性能提升 2 倍,再结合 Apache Doris 2.0 版本引入的冷热数据分层特性,整体性价比提升 10 倍以上。
+
+
+
+除了日志分析场景的优化以外,在复杂数据类型方面,我们增加了全新的数据类型
Map/Struct,包括支持以上类型的高效写入、存储、分析函数以及类型之间的相互嵌套,以更好满足多模态数据分析的支持。
+
+详细介绍:[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WJXKyudW8CJPqlUiAro_KQ](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WJXKyudW8CJPqlUiAro_KQ)
+
+## 高并发数据服务支持
+
+与复杂 SQL 和大规模 ETL 作业不同,在诸如银行交易流水单号查询、保险代理人保单查询、电商历史订单查询、快递运单号查询等 Data Serving
场景,会面临大量一线业务人员及 C 端用户基于主键 ID 检索整行数据的需求,在过去此类需求往往需要引入 Apache HBase 等 KV
系统来应对点查询、Redis 作为缓存层来分担高并发带来的系统压力。
+
+对于基于列式存储引擎构建的 Apache Doris 而言,此类的点查询在数百列宽表上将会放大随机读取 IO,并且执行引擎对于此类简单 SQL
的解析、分发也将带来不必要的额外开销,往往需要更高效简洁的执行方式。因此在新版本中我们引入了全新的行列混合存储以及行级
Cache,使得单次读取整行数据时效率更高、大大减少磁盘访问次数,同时引入了点查询短路径优化、跳过执行引擎并直接使用快速高效的读路径来检索所需的数据,并引入了预处理语句复用执行
SQL 解析来减少 FE 开销。
+
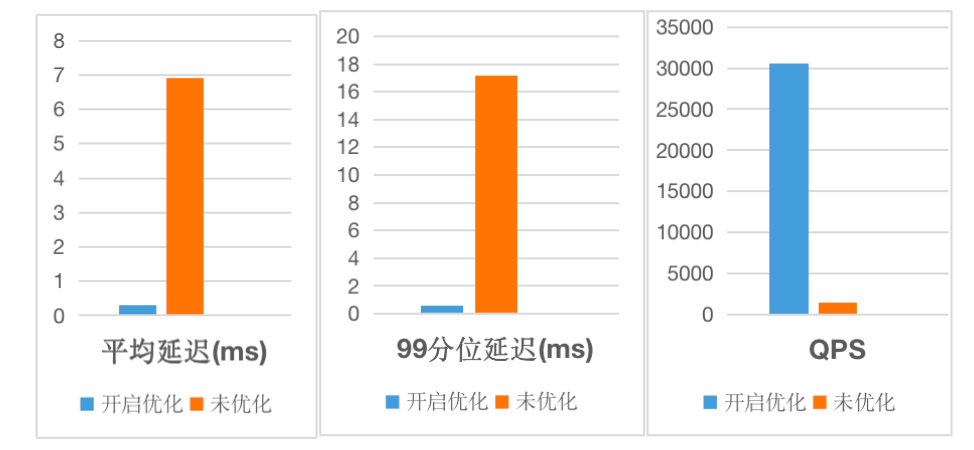
+通过以上一系列优化,**Apache Doris 2.0 版本在并发能力上实现了数量级的提升**!在标准 YCSB 基准测试中,单台 16 Core 64G
内存 4*1T 硬盘规格的云服务器上实现了单节点 30000 QPS 的并发表现,较过去版本点查询并发能力提升超 20 倍!基于以上能力,Apache
Doris 可以更好应对高并发数据服务场景的需求,替代 HBase 在此类场景中的能力,减少复杂技术栈带来的维护成本以及数据的冗余存储。
+
+
+
+参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/hight-concurrent-point-query](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/query-acceleration/hight-concurrent-point-query)
+
+详细介绍:[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ow77-kFMWXFxugFXjOPHhg](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ow77-kFMWXFxugFXjOPHhg)
+
+## 更全面、更高性能的数据湖分析能力
+
+在 Apache Doris 1.2 版本中,我们发布了 Multi-Catalog
功能,支持了多种异构数据源的元数据自动映射与同步,实现了数据湖的无缝对接。依赖 数据读取、执行引擎、查询优化器方面的诸多优化,在标准测试集场景下,Apache
Doris 在湖上数据的查询性能,较 Presto/Trino 有 3-5 倍的提升。
+
+在 2.0 版本中,我们进一步对数据湖分析能力进行了加强,不但支持了更多的数据源,同时针对用户的实际生产环境做了诸多优化,相较于 1.2
版本,能够在真实工作负载情况下显著提升性能。
+
+**更多数据源支持**
+
+- 支持 Hudi Copy-on-Write 表的 Snapshot Query 以及 Merge-on-Read 表的 Read Optimized
Query 和 Read Optimized Query,后续将支持 Incremental Query 和 Time
Traval。参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hudi](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hudi)
+
+- JDBC Catalog 新增支持 Oceanbase,目前支持包括
MySQL、PostgreSQL、Oracle、SQLServer、Doris、Clickhouse、SAP
HANA、Trino/Presto、Oceanbase
等近十种关系型数据库。参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/jdbc](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/jdbc)
+
+**数据权限管控**
+
+- 支持通过 Apache Range 对 Hive Catalog 进行鉴权,可以无缝对接用户现有的权限系统。同时还支持可扩展的鉴权插件,为任意
Catalog 实现自定义的鉴权方式。
参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hive](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/hive)
+
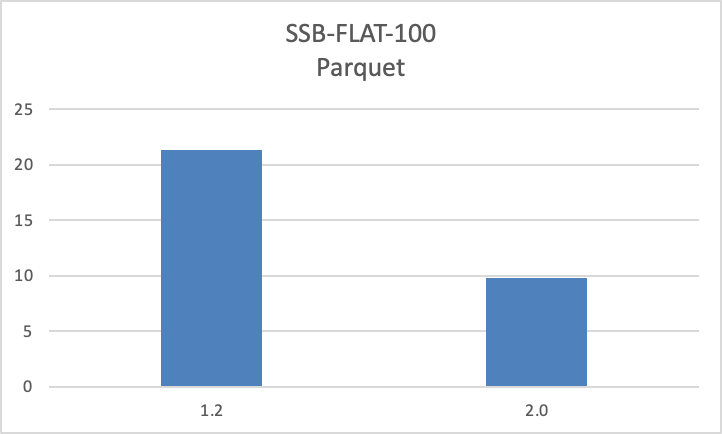
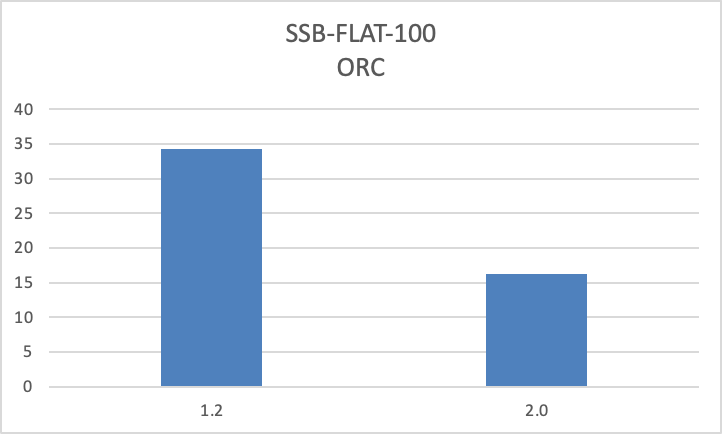
+**性能进一步优化,最高提升数十倍**
+- 优化了大量小文件场景以及宽表场景的读取性能。通过小文件全量加载、小 IO
合并、数据预读等技术,显著降低远端存储的读取开销,在此类场景下,查询性能最高提升数十倍。
+- 优化了 ORC/Parquet 文件的读取性能,相较于 1.2 版本查询性能提升一倍。
+
+
+
+
+- 支持湖上数据的本地文件缓存。可以利用本地磁盘缓存 HDFS
或对象存储等远端存储系统上的数据,通过缓存加速访问相同数据的查询。在命中本地文件缓存的情况下,通过 Apache Doris 查询湖上数据的性能可与
Apache Doris
内部表持平,该功能可以极大提升湖上热数据的查询性能。参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/filecache](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/filecache)
+
+- 支持外表的统计信息收集。和 Apache Doris 内表一样,用户可以通过 Analyze 语句分析并收集指定外表的统计信息,结合 Nereids
全新查询优化器,能够更准确更智能地对复杂 SQL 进行查询计划的调优。以 TPC-H 标准测试数据集为例,无需手动改写 SQL
即可获得最优的查询计划并获得更好的性能表现。
参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/lakehouse/multi-catalog/)
+
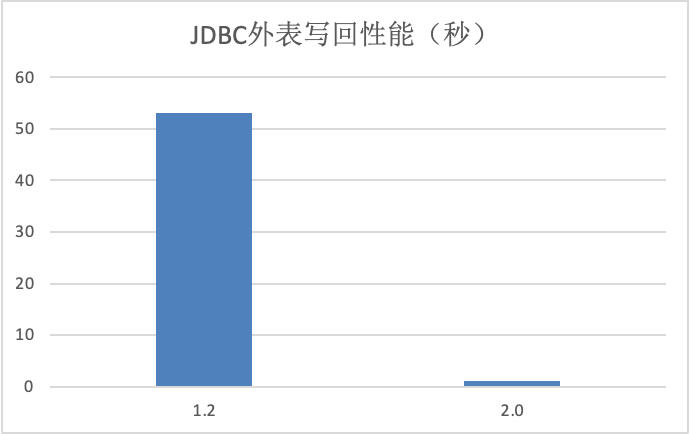
+- 优化了 JDBC Catalog 的数据写回性能。通过 PrepareStmt 和批量方式,用户通过 INSERT INTO 命令、通过 JDBC
Catalog 将数据写回到 MySQL、Oracle 等关系型数据库的性能提升数十倍。
+
+
+
+# 支持 Kubernetes 容器化部署
+
+在过去 Apache Doris 是基于 IP 通信的,在 K8s 环境部署时由于宿主机故障发生 Pod IP 漂移将导致集群不可用,在 2.0
版本中我们支持了 FQDN,使得 Apache Doris 可以在无需人工干预的情况下实现节点自愈,因此可以更好应对 K8s 环境部署以及灵活扩缩容。
+
+参考文档:[https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/install/k8s-deploy/](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/install/k8s-deploy/)
+
+# CCR 跨集群数据同步
+
+为了满足用户多集群之间数据同步的需求,在过去需要定期通过 Backup/Restore
命令进行数据备份和恢复,操作较为复杂、数据同步时延高并且还需要中间存储。为了满足用户多集群的数据库表自动同步需求,在 2.0-beta 版本中我们增加了
CCR 跨集群数据同步的功能,能够在库/表级别将源集群的数据变更同步到目标集群、以提升在线服务的数据可用性并更好地实现了读写负载分离以及多机房备份。
+
+参考文档:待补充
+
+# 其他升级注意事项
+
+- 1.2-lts 可以滚动升级到 2.0-beta,2.0-alpha 可以停机升级到 2.0-beta
+- 查询优化器开关默认开启 `enable_nereids_planner=true`;
+- 系统中移除了非向量化代码,所以 `enable_vectorized_engine` 参数将不再生效;
+- 新增参数 `enable_single_replica_compaction`;
+- 默认使用 datev2, datetimev2, decimalv3 来创建表,不支持 datev1,datetimev1, decimalv2 创建表;
+- 在 JDBC 和 Iceberg Catalog 中默认使用decimalv3;
+- date type 新增 AGG_STATE;
+- backend 表去掉 cluster 列;
+- 为了与 BI 工具更好兼容,在 show create table 时,将 datev2 和 datetimev2 显示为 date 和
datetime。
+- 在 BE 启动脚本中增加了 max_openfiles 和 swap 的检查,所以如果系统配置不合理,be 有可能会启动失败;
+- 禁止在 localhost 访问 FE 时无密码登录;
+- 当系统中存在 Multi-Catalog 时,查询 information schema 的数据默认只显示 internal catalog 的数据;
+- 限制了表达式树的深度,默认为 200;
+- array string 返回值 单引号变双引号;
+- 对 Doris的进程名重命名为 DorisFE 和 DorisBE;
+
+# 踏上 2.0 之旅
+
+距离 Apache Doris 2.0 Alpha
版本发布已经有一个半月之久,这一段时间内我们在加速核心功能特性开发的同时、还收获到了数百家企业对于新版本的切身体验与真实反馈,这些来自真实业务场景的反馈对于功能的打磨与进一步完善有着极大的帮助。因此
2.0-beta 版本无论在功能的完整度还是系统稳定性上,都已经具备了更佳的使用体验,欢迎所有对于 2.0 版本新特性有需求的用户部署升级。
+
+如果您在调研、测试以及部署升级 2.0 版本的过程中有任何问题,欢迎提交问卷信息,届时将由社区核心贡献者提供 1-1 专项支持。我们也期待 2.0
版本为更多社区用户提供实时统一的分析体验,相信 Apache Doris 2.0 版本会成为您在实时分析场景中的最理想选择。
+
+
---------------------------------------------------------------------
To unsubscribe, e-mail: commits-unsubscr...@doris.apache.org
For additional commands, e-mail: commits-h...@doris.apache.org
